Introduction to Cloud Services
Cloud services have revolutionized the methods of data storage, management, and access, significantly transforming industries and business models across the globe. These services encompass a variety of offerings available via the internet, ranging from fundamental storage solutions and computing capabilities to advanced software applications and development platforms. Hosted on physical infrastructure within data centers operated by cloud providers, these services enable users to utilize computing resources remotely without the need to oversee the underlying hardware. This transition to cloud technology allows users to interact with data and applications as if they were on a local device, while providing enhanced flexibility. The concept of cloud computing traces back to the utility computing model introduced in the 1960s, gaining traction with the rise of the internet. With major players like Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure making substantial investments in cloud infrastructure, these services have become indispensable across various industries.
How do cloud services work?
Cloud services refer to offerings provided by a cloud service provider, which involves the virtualization of software and applications stored on their physical servers located in large data centers. These virtualized services are accessible to customers via the Internet, allowing users to utilize applications and services without the need for extensive physical hardware or software installations on their devices. When data is saved “to the cloud,” it is stored on a remote server managed by the cloud service provider instead of on the organization’s own servers.
Typically, cloud service providers charge customers based on a monthly subscription or a pay-per-use model. This pricing structure can significantly reduce costs for organizations, as they are not required to host, manage, or maintain specific software within their own on-premises data centers.
Cloud services encompass a wide range of offerings, including servers, software applications, networks, databases, analytics tools, AI programs, and various online services for activities such as banking, shopping, and social interaction. Cloud service providers are responsible for hosting, managing, and maintaining data centers along with the associated storage, computing power, and networking resources. They also ensure the security of their physical hardware and offer certain security features for users accessing data and applications through the cloud.
Why use cloud services?
Utilizing cloud services allows you to delegate the management of infrastructure, enabling you to concentrate on leveraging the services themselves. The selected provider will facilitate various essential functions that ensure your business runs smoothly, including application processing, data exchange, storage, and management. With these services, your authorized personnel can engage in communication, collaboration, project management, and data analysis, processing, sharing, and storage without requiring oversight, maintenance, or backup from your IT department.
Core Types of Cloud Services
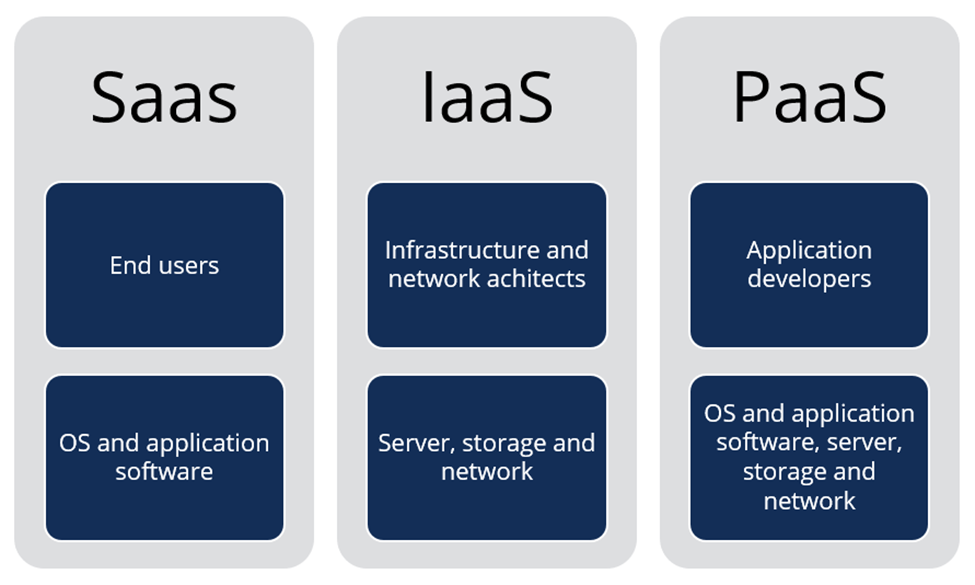
There are four main categories of cloud services, each designed for specific functions and offering distinct advantages:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS supplies virtualized computing resources, including storage, processing capabilities, and networking. This model enables organizations to lease these resources instead of purchasing physical hardware. Its high flexibility and scalability make IaaS particularly suitable for businesses with varying or unpredictable workloads.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
PaaS provides a development platform that enables developers to efficiently build, test, and deploy applications. By handling the underlying infrastructure, PaaS allows developers to concentrate on software creation rather than resource management. This service is especially advantageous in collaborative and agile development settings.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
SaaS delivers fully functional software applications via the internet, typically accessed through a web browser. Users benefit from not having to manage software updates or maintenance, as these responsibilities fall to the service provider. Common examples of SaaS include productivity software, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and email services.
Anything-as-a-Service (XaaS):
Anything-as-a-Service (XaaS) encompasses a wide range of cloud computing services that provide various resources and capabilities over the internet. This adaptable and scalable model allows organizations to access a diverse array of technology-related services, ranging from traditional infrastructure elements like computing power and storage (IaaS) to software applications (SaaS) and numerous other offerings in between.
Other Cloud Platform Types
1. Serverless computing
Serverless computing represents an architectural model in which a vendor oversees the deployment, management, and execution of code in response to customer demands. This approach transcends conventional methods of application development and server-based deployment. Users eliminate the need to purchase, lease, manage, provision, or maintain servers and virtual machines for backend code execution.
Billing for serverless computing is based on the precise amount of resources utilized in response to requests. Computing tasks are executed in brief intervals, with results stored for future access. Notable providers of serverless computing services include AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, IBM Cloud Functions, Microsoft Azure Functions, and Oracle Functions.
2. Function as a Service (FaaS)
Function as a Service (FaaS) represents a model of serverless computing that allows for the remote hosting of services, facilitating the deployment of functions in the cloud. In this model, functional code blocks are uploaded and triggered by designated events. FaaS eliminates the necessity for managing cloud infrastructure or application runtimes, as it does not utilize Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) resources.
Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud services can be implemented in various configurations to meet distinct business requirements, data needs, and security considerations:
- Public Cloud: A public cloud involves shared resources among numerous clients, managed by a third-party provider. It is typically the most economical and scalable solution, offering resources on an as-needed basis.
- Private Cloud: A private cloud is exclusively allocated to one organization and can be hosted either on-site or by a service provider, ensuring dedicated access. This model is preferred by companies with rigorous security or compliance demands.
- Hybrid Cloud: The hybrid cloud model merges public and private clouds, enabling organizations to store sensitive information on a private cloud while utilizing the public cloud for other operations. This strategy provides the advantages of both environments, including enhanced flexibility and cost efficiency.
- Multi-Cloud: Multi-cloud refers to the use of several public cloud providers to avoid dependency on a single vendor. This approach is particularly beneficial for ensuring resilience and meeting compliance standards, as well as for optimizing performance by choosing the most suitable cloud for each specific task.
Benefits of Cloud Services
Cloud computing presents a multitude of advantages, and specifically, cloud services can enhance these benefits while simplifying overall operations. Recent studies indicate that by 2025, around 51% of an organization’s IT budget will be allocated to the development and management of cloud-based systems. This marks a notable increase from 2022, when cloud system development and operations accounted for only 41% of the IT budget.
Businesses are particularly drawn to cloud services for several reasons, including:
- Scalability: Cloud services provide effortless scalability, allowing organizations to adjust resources in response to real-time demand. This capability enables businesses to manage varying workloads effectively and avoid unnecessary costs for unused resources.
- Cost Efficiency: By eliminating the need for physical hardware, cloud services significantly lower the expenses related to infrastructure maintenance and upgrades. Many cloud models operate on a pay-as-you-go basis, facilitating better budget management for companies.
- Flexibility and Mobility: With cloud services accessible from any device connected to the internet, teams can work from virtually anywhere, enhancing flexibility and supporting remote work initiatives. This accessibility fosters real-time collaboration, enabling multiple users to engage with the same data or application simultaneously.
- Business Continuity: Many cloud providers offer disaster recovery solutions, ensuring that data is securely backed up and can be restored in the event of hardware failures or cyberattacks. This capability helps organizations maintain operations and minimize downtime during crises.
- Access to Advanced Technologies: Cloud services grant businesses access to state-of-the-art technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and machine learning tools, empowering them to innovate without the need for substantial investments in research or infrastructure.
How are cloud services used?
In today’s digital landscape, the utilization of cloud services has become incredibly diverse, with countless options available. Most businesses provide online functionalities, ranging from basic account access to more complex services. Customers now anticipate that organizations will deliver user-friendly cloud solutions for scheduling appointments, making purchases, transferring money, receiving medical test results, checking academic grades, enrolling in courses, ordering prescriptions, and a variety of other tasks.
This trend is not limited to consumer-facing services; enterprises also frequently leverage cloud solutions.
Below are some of the prevalent cloud services adopted by contemporary organizations:
- Email – Today, a majority of individuals rely on cloud-based services for their email needs, even when their organization maintains an email server. This preference stems from the desire for flexibility, as employees want to access their emails on various devices and from any location at any time. Cloud email services facilitate seamless communication among colleagues.
- Collaboration services – Platforms like Slack and WebEx provide chat and file-sharing capabilities, enabling work teams to communicate and collaborate effectively, regardless of their physical locations.
- Meeting services – Online meeting tools function similarly to collaboration services, allowing organizations to convene with clients, colleagues, partners, investors, and other stakeholders from around the globe.
- Big data analytics – Data serves as a vital asset for organizations, and contemporary analytics tools empower leaders to extract essential insights regarding their operations, processes, products, and more, helping them identify opportunities for efficiency and cost savings.
- Software development – Numerous cloud services support software and application development, which is essential for organizations aiming to deliver the online services that their customers demand.
- AI and machine learning platforms – The integration of AI and machine learning technologies is becoming more prevalent in enterprise environments, as organizations leverage these advanced tools to tackle their most pressing challenges.
- Data backup and recovery – Many organizations opt for online backup and recovery solutions provided by third-party vendors to safeguard their data and applications, ensuring availability in the event of a security breach or system failure.
- Security and compliance – Certain providers offer user-friendly online security and compliance solutions that assist organizations in meeting the increasingly complex and evolving security and privacy regulations.
Key Security Considerations
Cloud services present numerous benefits; however, they also introduce security challenges that organizations must tackle:
- Data Privacy and Compliance: It is crucial for companies to verify that their cloud service providers adhere to data protection laws, such as GDPR or HIPAA, relevant to their sector. Implementing robust data privacy protocols is vital for safeguarding sensitive information, often necessitating enhanced encryption and stringent access controls.
- Access Control and Authentication: Establishing rigorous access controls and employing multi-factor authentication are essential for securing cloud resources. Unauthorized access poses a significant risk of data breaches, making effective credential management imperative.
- Data Ownership and Control: While cloud providers generally oversee data management, ownership remains with the businesses. Organizations must have explicit agreements outlining data access, deletion, and retention policies to mitigate compliance and operational risks.
- Vendor Lock-In: Transitioning data between providers or reverting to on-premises solutions can be complex, a situation referred to as “vendor lock-in.” To mitigate this risk, organizations frequently adopt multi-cloud strategies or ensure their systems are compatible with various platforms.
Cloud Management and Optimization
Effective cloud management enables organizations to fully leverage the advantages of cloud services while maintaining cost control. Essential management practices include:
- Monitoring and Analytics: Monitoring solutions assess resource utilization, performance indicators, and potential security vulnerabilities. Analytics deliver insights for optimization, ensuring efficient resource deployment.
- Automated Scaling: Implementing automated scaling allows organizations to dynamically adjust resources in response to demand fluctuations, which is particularly beneficial for applications experiencing variable traffic.
- Cost Optimization Tools: Numerous cloud providers supply integrated tools for tracking expenditures, optimizing resource use, and predicting costs. These cost optimization strategies assist businesses in adhering to budgets and making informed decisions regarding cloud investments.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Services
As cloud computing evolves, several key trends are influencing the future landscape of cloud services:
- Edge Computing: This approach brings data processing closer to its source, which minimizes latency and enhances response times for applications requiring real-time data. It is increasingly adopted in Internet of Things (IoT) applications, autonomous vehicles, and smart city infrastructures.
- Serverless Computing: This model enables developers to create and deploy applications without the need to manage servers. By allowing the service provider to handle server maintenance, it streamlines the development process and reduces operational burdens.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Cloud platforms are incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning functionalities to improve data processing and decision-making capabilities. These sophisticated tools empower organizations to analyze extensive datasets and derive insights more efficiently.
- Sustainability Efforts: Cloud service providers are prioritizing sustainability by establishing energy-efficient data centers and utilizing renewable energy sources. This initiative is crucial as cloud data centers increasingly contribute to global energy consumption.
Conclusion
Cloud services play a crucial role in contemporary technology, reshaping our approaches to work, innovation, and collaboration. Offering tailored solutions for infrastructure, platform development, and comprehensive software, these services deliver flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Despite ongoing security and management challenges, innovations in cloud technologies—such as edge computing, serverless architectures, and artificial intelligence—are expanding the potential of cloud computing. As these services advance, organizations can utilize these resources to maintain agility and competitiveness in a rapidly digitalizing environment, paving the way for future growth and innovation.

